overall view about the different functions of lighthouses (selection)
sign |
diagram |
course differing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
to port (left) |
none |
to starboard (right) |
||
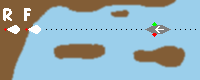
leading lights |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Leading lights mark the course. They consist of the lower front light (F) near the
coast and the higher rear light (R) deeper in land. If the course is correct, the rear light is
exactly above the front light. If the course isn't correct, both lights are visible side by
side.
***
sign |
diagram |
course differing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
to port (left) |
none |
to starboard (right) |
||
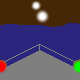
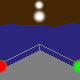
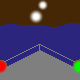
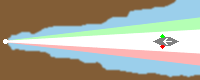
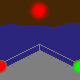
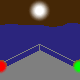
direction light |
 |
 |
 |
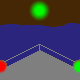 |
A direction light has the same function like a leading light (see above): mark the
course. Such light has three sectors, the middle one (here white) marks the course, called
leading sector. The both outer sectors (warning sectors) show with their colored light, that the
course isn't right.
***
sign |
diagram |
air obstruction light |
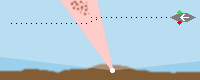 |
An air obstruction light marks dangerous areas with a red sector, uncertain
areas are mostly marked with green sectors. The light with its colored sectors warns the skipper
to be careful.
***
sign |
diagram |
cross light |
 |
Cross lights are shining across to the course. Their middle sector mark the point to
change the course. The other colored outer sectors announce the changing of
course.
***
sign |
diagram |
pier or |
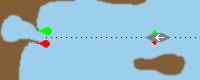 |
Pier or breakwater lights mark the entry to a port or harbour. One, mostly two
breakwaters protect a port. A green pier light shines at the right head of pier
(starboard) and a red one at the left head (port).
***
sign |
diagram |
lighthouse |
 |
These lighthouses support the orientation at sea. They can identified by their
light character and stand mostly at exposed positions.
***